cervical vertebrae compression test|special test for cervical spine : makers Doctors routinely use the Spurling test to check for cervical radiculopathy, which is the medical term for a compressed or pinched nerve in the neck. Cervical radiculopathy is common.
Falaremos sobre alta performance física e mental; como os hábitos te aproximam - ou distanciam - dos bons resultados; aspectos da neurociência e da psicologia relacionados ao seu desempenho e muito mais! Hosts: Bruno Perini @bruno_perini e Malu Perini @maluperini. Convidados: Paulo Muzy @paulomuzy e Eslen Delanogare .
{plog:ftitle_list}
A Amorscore abrange centenas de ligas de futebol, copas e campeonatos, fornecendo resultados atualizados em tempo real, dados estatísticos, tabelas de classificação, destaques em vídeo e agendas. Desde as ligas de futebol mais populares (UEFA Champions League, UEFA Europa League, Premier League, LaLiga, etc.) até avaliações .
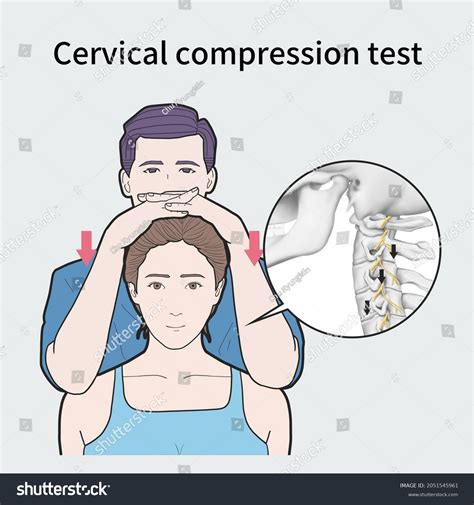
The Spurling Test is designed to reproduce symptoms by compression of the affected nerve root. The cervical extension is used to induce/reproduce posterior bulging of the . The Spurling test helps to diagnose cervical radiculopathy. It’s also called the Spurling compression test or Spurling maneuver.
If you think you have a pinched nerve, or cervical radiculopathy, a positive Spurling test can help your doctor with a diagnosis. The Spurling test has been proven to be . The Spurling test is used to detect cervical radiculopathy. There is no standard protocol for administering the Spurling test and there are multiple variations that include different motions and sequences of motions. The Spurling test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess cervical nerve compression and radiculopathy. By reproducing or worsening symptoms through specific . Doctors routinely use the Spurling test to check for cervical radiculopathy, which is the medical term for a compressed or pinched nerve in the neck. Cervical radiculopathy is common.
After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and .The Spurling test is one of the best-known and most widely used provocative tests for the assessment of the cervical spine. The Spurling test was originally named as Spurling’s neck .Spinal cord compression can occur anywhere from your neck (cervical spine) down to your lower back (very top of lumbar spine). Symptoms include numbness, pain, weakness, and loss of bowel and bladder control. Depending on the cause of the compression, symptoms may develop suddenly or gradually.
(2,3) The test is most commonly defined in current literature as passive cervical extension, ipsilateral rotation, and axial compression. (4) This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients . What is the Spurling test? The Spurling test is a physical assessment to diagnose cervical radiculopathy or a pinched nerve in your neck. If you experience neck pain, a healthcare provider may offer this test.The Spurling test can tell your provider if something is squeezing or pressing against a nerve (nerve root compression) in your cervical spine.Spurling’s Test for Cervical Radicular Syndrome / Cervical Radiculopathy. Spurling’s test is a test with a low sensitivity of 50% and a good specificity of 83% to diagnose cervical radicular syndrome according to Wainner et al. (2003).Several authors have shown that this test has a rather low sensitivity and a high specificity.
what is deep neck compression
Your cervical spine is the first seven stacked vertebral bones of your spine. This region is more commonly called your neck. . These tests help determine ongoing nerve damage and the site of nerve compression. Myelogram. This imaging test examines the relationship between your vertebrae and disks, outlines the spinal cord and nerves exiting . Discectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of a disk to relieve pressure off nearby roots.; Corpectomy: A corpectomy involves removing part or all the vertebral body to decompress the spinal cord and nerves. This procedure is usually performed with some form of discectomy. Laminotomy or laminectomy: A laminotomy involves removal of the lamina, the .
Cervical Spine Tests That Provide or Relieve Pain Spurling Neck Compression Test . Spurling and Scoville first described the Spurling neck compression test, also known as the foraminal compression test, neck compression test, or quadrant test, in 1944 as “the most important diagnostic test and one that is almost pathognomonic of a cervical intraspinal lesion.”
cervical spine C6 nerve root travels under C5 pedicle (mismatch) lumbar spine L5 nerve root travels under L5 pedicle (match) . foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy. performed by rotating head toward the affected side, extending the neck, and then applying and axial load (downward .
Pages in category "Cervical Spine - Special Tests" The following 11 pages are in this category, out of 11 total. B. Bakody Sign; C. Canadian C-Spine Rule; Cervical Distraction Test; Cervical Flexion-Rotation Test; Cervical rotation lateral flexion test; Cranio‐cervical Flexion Test; H. Hoffmann's Sign; S.
• Brachial Plexus Tension Test • Cervical Flexion (including Brudzinski’s Sign, Lhermitte’s sign, Lindner’s sign) • Cervical Flexion Rotation Test • Cervical Compression, Jackson’s Compression, Maximum Foraminal Compression(Spurling’s) • Cervical Distraction • Cervical Resisted Muscle Tests and Passive Range of Motion (O .Better, is to use these 4 clinical tests: Spurlings Test, Upper limb tension-1 Distraction test and Cervical Flexion Rotation Test. When all 4 of these clinical test are positive, the post-test probability of cervical radiculopathy is 90%. . Validity of clinical tests in the diagnosis of root compression in cervical disc disease. Spine (Phila . The Maximum Cervical compression test is used to detect nerve root involvement in the cervical spine. This test is also known by other names, including the Foraminal Compression test and Spurling’s test. This test should not be used if a significant cervical injury is suspected.
Cervical radiculopathy happens when a nerve root in your neck (cervical spine) becomes compressed (pinched) and inflamed. This compression has two main causes: Degenerative changes that happen in your spine as you age (cervical spondylosis). A herniated (bulging) disk in your neck. Cervical spondylosis and cervical radiculopathyCervical stenosis is one such degenerative condition that may affect the spinal cord and lead to compromised coordination of the extremities. When diagnosing cervical stenosis, doctors must determine whether progressive dysfunction (myelopathy) is present as a result of the spinal cord compression. See Cervical Stenosis with Myelopathy Cervical radiculopathy is a clinical condition characterized by unilateral arm pain, numbness and tingling in a dermatomal distribution in the hand, and weakness in specific muscle groups associated with a single .
Some people with cervical spondylosis benefit from the use of traction, which can help provide more space within the spine if nerve roots are being pinched. Surgery If conservative treatment fails or if neurological symptoms — such as weakness in your arms or legs — worsen, you might need surgery to create more room for your spinal cord and . This test works when your doctor flexes your cervical spine. If you feel a shock-like pain or feeling down your spine or arms and legs, you’ll get a positive test. Hoffman’s sign.Neck pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal conditions with a high personal and economic burden.[1][2] Clinicians will often encounter patients with neck pain and other cervical spine conditions. It is, therefore, essential that they can confidently perform a thorough assessment of the cervical spine. This page provides a step-by-step overview of the .
neck pain with radiating pain/cervical radiculopathy, including the upper limb tension test, Spurling's test, distraction test, and the Valsalva test. Cranial cervical flexion and neck flexor muscle endurance tests may be use in assessing movement coordination impairments, and algometric assessment of pressure pain threshold may be useful in . Cervical Myelopathy is a common form of neurologic impairment caused by compression of the cervical spinal cord most commonly due to degenerative . tandem stenosis occurs in lumbar and cervical spine in ~20% of patients. . test is positive when extreme cervical flexion leads to electric shock-like sensations that radiate down the spine and .The spine is made up of 24 bones, called vertebrae, that are stacked on top of one another. These bones connect to create a canal that protects the spinal cord. The seven small vertebrae that begin at the base of the skull and form the neck comprise (make up) the cervical spine.
Flexion compression test. Procedure: The patient is seated. The examiner stands behind the patient and passively moves the cervical spine into flexion (tilts the patient’s head forward). Then axial compression is applied to the top of the head. Assessment: This is a good test of the integrity of the intervertebral disk.The caption reads Cervical degenerative dysstructure: The progressive nature of cervical instability that leads to a breakdown of the cervical curve resulting in destructive forces (compression, grinding, and impingement of blood vessels and nerves) being placed on vital neurovascular structures including the cervical spinal cord and vagus nerves.
Cervical spine canal stenosis, whether of bony or soft-tissue origins, can cause lower-extremity signs and symptoms. Most notable is long tract pain, or rhizalgia, appearing in an ipsilateral leg . Spurling compression test: Dural sheath, nerve root, spinal nerve: Radicular pain: Maximal foraminal compression test: Dural sheath, nerve root . Learn about the Spurling test, a diagnostic maneuver used to assess cervical nerve compression and radiculopathy. Understand the procedure, interpretation, and significance of this test in diagnosing cervical spine conditions and guiding appropriate treatment decisions.
There are seven cervical vertebrae and eight cervical nerve roots. The spinal cord is the extension of the central nervous system outside the cranium. It is encased by the vertebral column and begins at the foramen magnum. The spinal cord is an extremely vital part of the central nervous system, and even a small injury can lead to severe disability.. A complex .
special test for cervical spine
Degenerative cervical myelopathy is the most common degenerative, nontraumatic, and progressive form of spinal cord compression worldwide. 3, 10, 13, 14 It is also recognized as the leading cause .
bat failed compression test
bat roller and compression tester
bbcor bat compression test
positive spurling sign
Omegle (oh·meg·ull) provides an excellent opportunity to make new friends, especially during social distancing. Engage in one-on-one conversations with randomly paired .
cervical vertebrae compression test|special test for cervical spine